2.3 Pop操作
- Pop操作:
- 移除栈顶元素
- 时间复杂度:
- 实现步骤:
- 检查栈是否为空
- 获取栈顶元素
- 栈顶指针减1
- 返回之前的栈顶元素
- 示例代码:
void pop() {
if (top < 0) {
cout << "Stack Underflow" << endl;
return;
}
top--;
}
Pop操作示意图:
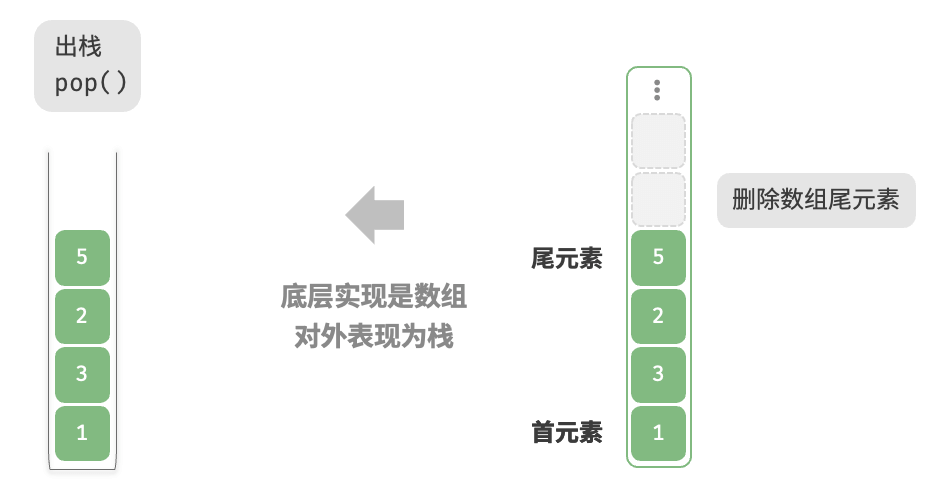
注意事项:
- 必须检查栈是否为空
- 弹出元素后,该位置的内存仍然保留原值
- 但该位置逻辑上已不属于栈
- 连续pop操作会按照LIFO顺序删除元素
2.4 Top操作
Top操作:
- 返回栈顶元素但不移除
- 时间复杂度:
实现步骤:
- 检查栈是否为空
- 返回栈顶元素的值
示例代码:
int top() {
if (top < 0) {
cout << "Stack is Empty" << endl;
return -1;
}
return arr[top];
}
注意事项:
- 与pop操作不同,top操作不会修改栈的状态
- 常用于需要查看栈顶元素但不想移除它的场景
- 在某些实现中也称为peek操作
2.5 其他操作
- Empty操作:
- 检查栈是否为空
- 时间复杂度:
bool isEmpty() {
return (top < 0);
}
- Size操作:
- 返回栈中元素的数量
- 时间复杂度:
int size() {
return top + 1;
}
- isFull操作(数组实现时):
- 检查栈是否已满
- 时间复杂度:
bool isFull() {
return (top == capacity - 1);
}
- Clear操作:
- 清空栈中所有元素
- 时间复杂度:
void clear() {
top = -1;
}
3. 栈的实现方式
3.1 数组实现栈
- 数组实现栈的基本思路:
- 使用一维数组存储栈元素
- 使用一个变量跟踪栈顶位置
- 入栈和出栈操作通过移动栈顶指针实现
- 优点:
- 实现简单直观
- 随机访问速度快
- 内存布局连续,缓存友好
- 缺点:
- 需要预先分配空间
- 可能会导致空间浪费
- 栈满时需要扩容(动态数组)
完整实现代码:
class ArrayStack {
private:
int* arr;
int top;
int capacity;
public:
ArrayStack(int size) {
arr = new int[size];
capacity = size;
top = -1;
}
~ArrayStack() {
delete[] arr;
}
void push(int x) {
if (isFull()) {
cout << "Stack Overflow" << endl;
return;
}
arr[++top] = x;
}
int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Stack Underflow" << endl;
return -1;
}
return arr[top--];
}
int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) return -1;
return arr[top];
}
bool isEmpty() { return top == -1; }
bool isFull() { return top == capacity - 1; }
int size() { return top + 1; }
};
3.2 链表实现栈
- 链表实现栈的基本思路:
- 使用单链表存储栈元素
- 将链表的头部作为栈顶
- 入栈和出栈操作在链表头部进行
- 优点:
- 动态分配内存,不需要预先确定大小
- 不存在栈满的问题
- 空间利用率高
- 缺点:
- 需要额外的内存存储指针
- 操作稍微复杂
- 不支持随机访问
完整实现代码:
class LinkedListStack {
private:
struct Node {
int data;
Node* next;
Node(int d) : data(d), next(nullptr) {}
};
Node* top;
int stackSize;
public:
LinkedListStack() : top(nullptr), stackSize(0) {}
~LinkedListStack() {
while (!isEmpty()) {
pop();
}
}
void push(int x) {
Node* newNode = new Node(x);
newNode->next = top;
top = newNode;
stackSize++;
}
int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Stack Underflow" << endl;
return -1;
}
int value = top->data;
Node* temp = top;
top = top->next;
delete temp;
stackSize--;
return value;
}
int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) return -1;
return top->data;
}
bool isEmpty() { return top == nullptr; }
int size() { return stackSize; }
};
3.3 STL stack使用
- C++ STL stack:
- C++标准库提供的栈容器适配器
- 默认基于deque实现,也可基于vector或list
- 提供完整的栈操作接口
- STL stack的主要操作:
push():将元素压入栈顶pop():移除栈顶元素top():返回栈顶元素empty():检查栈是否为空size():返回栈中元素个数
- 注意事项:
pop()不返回被删除的元素- 使用
top()前应确保栈非空 - 可以指定底层容器:
stack<int, vector<int>> s; stack<int, list<int>> s; - STL stack是容器适配器,不支持迭代器
3.3 STL stack使用(续)
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
usng namespace std;
int main() {
stack<int> s;
// 向栈中添加元素
s.push(10);
s.push(20);
s.push(30);
// 打印栈顶元素
cout << "Top element is: " << s.top() << endl; // 输出: Top element is: 30
// 移除栈顶元素
s.pop();
cout << "After popping, top element is: " << s.top() << endl; // 输出: After popping, top element is: 20
// 检查栈是否为空
if (!s.empty()) {
cout << "Stack is not empty." << endl; // 输出: Stack is not empty.
}
// 打印栈的大小
cout << "Size of stack: " << s.size() << endl; // 输出: Size of stack: 2
// 继续移除元素
s.pop();
s.pop();
// 检查栈是否为空
if (s.empty()) {
cout << "Stack is empty." << endl; // 输出: Stack is empty.
}
return 0;
}
3.4 栈的实现比较
| 特性 | 数组实现 | 链表实现 | STL stack |
|---|---|---|---|
| 内存分配 | 静态/预分配 | 动态分配 | 动态分配 |
| 空间效率 | 可能浪费 | 高效 | 高效 |
| 时间效率 | 操作O(1) | 操作O(1) | 操作O(1) |
| 实现复杂度 | 简单 | 中等 | 最简单(直接使用) |
| 扩展性 | 有限 | 良好 | 良好 |
| 缓存友好性 | 高 | 低 | 中等 |
| 适用场景 | 大小可预测 | 大小不可预测 | 一般用途 |
| 溢出风险 | 有栈溢出风险 | 无栈溢出风险 | 无栈溢出风险 |
选择建议:
- 对于大小已知且较小的栈,可以使用数组实现
- 对于大小不确定或可能很大的栈,使用链表实现
- 对于一般应用,推荐使用STL stack
4. 栈的应用场景
4.1 函数调用
- 函数调用栈:
- 存储函数调用的上下文信息
- 管理函数的局部变量
- 处理函数的返回
- 工作原理:
- 调用函数时压栈:
- 返回地址
- 参数
- 局部变量
- 函数返回时出栈:
- 恢复调用点
- 清理局部变量
- 获取返回值
- 调用函数时压栈:
示例代码:
void function3() {
int x = 3;
// 函数3的栈帧在最顶部
}
void function2() {
int y = 2;
function3(); // 调用function3
// function3返回后继续执行
}
void function1() {
int z = 1;
function2(); // 调用function2
// function2返回后继续执行
}
int main() {
function1(); // 调用function1
return 0;
}
4.2 表达式求值
- 表达式求值应用:
- 计算算术表达式
- 处理运算符优先级
- 转换表达式格式(中缀转后缀)
- 实现思路:
- 使用两个栈:
- 运算符栈
- 操作数栈
- 遍历表达式:
- 数字直接入操作数栈
- 运算符按优先级处理
- 计算结果:
- 弹出运算符和操作数
- 执行运算
- 结果压回操作数栈
- 使用两个栈:
示例代码:
int evaluateExpression(string expr) {
stack<int> values;
stack<char> ops;
for (int i = 0; i < expr.length(); i++) {
if (isdigit(expr[i])) {
int val = 0;
while (i < expr.length() &&
isdigit(expr[i])) {
val = val * 10 + (expr[i] - '0');
i++;
}
i--;
values.push(val);
}
else if (expr[i] == '(') {
ops.push(expr[i]);
}
else if (expr[i] == ')') {
while (!ops.empty() &&
ops.top() != '(') {
int val2 = values.top();
values.pop();
int val1 = values.top();
values.pop();
char op = ops.top();
ops.pop();
values.push(applyOp(val1, val2, op));
}
ops.pop(); // 弹出'('
}
else if (expr[i] == '+' ||
expr[i] == '-' ||
expr[i] == '*' ||
expr[i] == '/') {
while (!ops.empty() &&
precedence(ops.top()) >=
precedence(expr[i])) {
int val2 = values.top();
values.pop();
int val1 = values.top();
values.pop();
char op = ops.top();
ops.pop();
values.push(applyOp(val1, val2, op));
}
ops.push(expr[i]);
}
}
while (!ops.empty()) {
int val2 = values.top();
values.pop();
int val1 = values.top();
values.pop();
char op = ops.top();
ops.pop();
values.push(applyOp(val1, val2, op));
}
return values.top();
}
4.3 括号匹配
- 括号匹配问题:
- 检查括号是否正确配对
- 支持多种类型的括号
- 常见于代码编辑器和编译器
- 实现思路:
- 遇到左括号时入栈
- 遇到右括号时:
- 检查栈是否为空
- 检查栈顶括号是否匹配
- 匹配则出栈
- 最后检查栈是否为空
示例代码:
bool isValid(string s) {
stack<char> st;
for (char c : s) {
if (c == '(' || c == '{' || c == '[') {
st.push(c);
}
else {
if (st.empty()) return false;
if (c == ')' && st.top() != '(')
return false;
if (c == '}' && st.top() != '{')
return false;
if (c == ']' && st.top() != '[')
return false;
st.pop();
}
}
return st.empty();
}
4.4 其他应用场景
- 深度优先搜索(DFS):
- 使用栈存储待访问的节点
- 实现回溯功能
- 图和树的遍历
- 撤销操作:
- 存储操作历史
- 实现Undo/Redo功能
- 文本编辑器的实现
- 浏览器历史:
- 前进/后退功能
- 网页访问记录
- 会话管理
- 内存管理:
- 函数调用栈
- 程序执行上下文
- 异常处理
- 编译器实现:
- 语法分析
- 表达式求值
- 代码生成
5. 经典例题
5.1 括号匹配问题
POJ 1426. Find The Multiple
问题描述:
给定一个括号序列,包含小括号'('和')',判断该序列是否合法。合法的定义是每个左括号都有一个对应的右括号,且括号序列正确嵌套。
解题思路:
- 使用栈存储左括号
- 遇到右括号时检查栈顶是否匹配
- 最后检查栈是否为空
完整代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
bool isValid(string s) {
stack<char> st;
for (char c : s) {
if (c == '(') {
st.push(c);
} else if (c == ')') {
if (st.empty()) return false;
st.pop();
}
}
return st.empty();
}
int main() {
string s;
while (cin >> s) {
if (isValid(s)) {
cout << "YES" << endl;
} else {
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
5.2 中缀表达式转后缀
HDU 1237. 简单计算器
问题描述:
实现一个简单的计算器,支持加减乘除四种运算,没有括号。
解题思路:
- 使用栈将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式
- 使用栈计算后缀表达式的值
- 处理运算符优先级
- 处理连续的数字和运算符
示例:
输入:3 + 5 * 2
输出:13
5.2 代码示例
实现代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int calculate(string s) {
stack<int> nums;
stack<char> ops;
stringstream ss(s);
int num;
char op;
// 读取第一个数字
ss >> num;
nums.push(num);
while (ss >> op) {
if (op == '0') break;
// 读取下一个数字
ss >> num;
// 根据运算符优先级处理
if (op == '+' || op == '-') {
while (!ops.empty()) {
char top_op = ops.top();
ops.pop();
int b = nums.top(); nums.pop();
int a = nums.top(); nums.pop();
if (top_op == '+') nums.push(a + b);
else if (top_op == '-') nums.push(a - b);
else if (top_op == '*') nums.push(a * b);
else if (top_op == '/') nums.push(a / b);
}
ops.push(op);
} else { // * 或 /
while (!ops.empty() && (ops.top() == '*' || ops.top() == '/')) {
char top_op = ops.top();
ops.pop();
int b = nums.top(); nums.pop();
int a = nums.top(); nums.pop();
if (top_op == '*') nums.push(a * b);
else nums.push(a / b);
}
ops.push(op);
}
nums.push(num);
}
// 处理剩余的运算符
while (!ops.empty()) {
char top_op = ops.top();
ops.pop();
int b = nums.top(); nums.pop();
int a = nums.top(); nums.pop();
if (top_op == '+') nums.push(a + b);
else if (top_op == '-') nums.push(a - b);
else if (top_op == '*') nums.push(a * b);
else if (top_op == '/') nums.push(a / b);
}
return nums.top();
}
int main() {
string s;
while (getline(cin, s) && s != "0") {
cout << calculate(s) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
5.3 直方图最大矩形
POJ 2559. 直方图中最大的矩形
问题描述:
给定 n 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
解题思路:
- 使用单调栈
- 栈中存储柱子的索引
- 当前柱子高度小于栈顶时计算面积
- 维护递增的高度序列
实现代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
stack<int> st;
heights.push_back(0); // 添加哨兵
LL maxArea = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) {
while (!st.empty() && heights[st.top()] > heights[i]) {
int height = heights[st.top()];
st.pop();
int width = st.empty() ? i : i - st.top() - 1;
maxArea = max(maxArea, (LL)height * width);
}
st.push(i);
}
heights.pop_back(); // 移除哨兵
return maxArea;
}
int main() {
int n;
while (cin >> n && n != 0) {
vector<int> heights(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> heights[i];
}
cout << largestRectangleArea(heights) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
5.4 单调栈应用
CSES 1645. 最近的较小值
问题描述:
给定一个包含n个整数的数组。对于每个位置,找出位于其左侧的第一个比当前值小的元素的位置。如果不存在这样的元素,输出0。
解题思路:
- 使用单调栈维护左侧的元素
- 对于每个新元素:
- 弹出栈中所有大于等于当前元素的值
- 栈顶即为左侧第一个较小值
- 维护单调递增栈
实现代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> arr(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> arr[i];
}
// 使用pair存储值和索引
stack<pair<int,int>> st;
vector<int> result(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 弹出所有大于等于当前值的元素
while (!st.empty() && st.top().first >= arr[i]) {
st.pop();
}
// 如果栈为空,说明左侧没有更小的值
if (st.empty()) {
result[i] = 0;
} else {
// 栈顶元素即为左侧第一个较小值
result[i] = st.top().second + 1;
}
// 将当前元素入栈
st.push({arr[i], i});
}
// 输出结果
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << result[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
示例:
输入:
8
2 5 1 4 8 3 2 5
输出:
0 1 0 3 4 3 3 7
6. 优化技巧
6. 优化技巧
- 空间优化:
- 使用动态数组实现栈,根据需要调整容量
- 使用内存池减少频繁的内存分配和释放
- 考虑使用压缩技术存储特定类型的数据
- 时间优化:
- 避免不必要的复制操作
- 使用移动语义(C++11)提高效率
- 预分配足够的空间避免频繁扩容
- 常见陷阱:
- 栈为空时进行pop或top操作
- 忽略栈满的情况(数组实现)
- 内存泄漏(链表实现)
- 递归调用过深导致栈溢出
- 特殊优化:
- 双栈技术:使用两个栈实现队列
- 最小栈:O(1)时间获取栈中最小元素
- 栈的批量操作:减少函数调用开销
7. 总结
7. 总结
核心要点:
- 栈的基本概念
- 后进先出(LIFO)原则
- 只能在栈顶进行操作
- 受限的线性数据结构
- 栈的基本操作
- push:入栈
- pop:出栈
- top:查看栈顶
- empty:检查是否为空
- size:获取元素个数
- 栈的实现方式
- 数组实现
- 链表实现
- STL stack
应用场景:
- 函数调用管理
- 表达式求值
- 括号匹配
- 深度优先搜索
- 撤销操作
- 浏览器历史
- 编译器实现
经典例题:
- 有效的括号
- 中缀表达式转后缀
- 直方图最大矩形
- 每日温度问题
8. 练习题目
8.1 初级练习题
-
[HDU 1062] Text Reverse
- 难度:★★☆☆☆
- 描述:将一行文本中的每个单词反转,但保持单词的顺序不变
- 思路:使用栈存储每个单词的字符,然后弹出实现反转
-
[POJ 1363] Rails
- 难度:★★☆☆☆
- 描述:判断给定的出栈序列是否可能通过特定的入栈序列得到
- 思路:模拟入栈出栈过程,检查是否能得到目标序列
-
[CSES 1619] Restaurant Customers
- 难度:★★☆☆☆
- 描述:给定顾客的到达和离开时间,计算餐厅同时最多有多少顾客
- 思路:使用栈或优先队列处理时间点,模拟顾客进出
8.2 中级练习题
-
[POJ 3250] Bad Hair Day
- 难度:★★★☆☆
- 描述:计算每头牛能看到右边多少头牛的背部
- 思路:使用单调栈维护可见的牛的高度
-
[HDU 4699] Editor
- 难度:★★★☆☆
- 描述:实现一个简单的文本编辑器,支持插入、删除和撤销操作
- 思路:使用栈存储操作历史,实现撤销功能
-
[CSES 1142] Advertisement
- 难度:★★★☆☆
- 描述:在广告牌上找出最大的矩形面积
- 思路:类似直方图最大矩形问题,使用单调栈解决
8.3 高级练习题
-
[POJ 2082] Terrible Sets
- 难度:★★★★☆
- 描述:给定一系列矩形的宽度和高度,求能形成的最大矩形面积
- 思路:使用单调栈,类似直方图最大矩形问题
-
[CSES 1076] Sliding Median
- 难度:★★★★☆
- 描述:计算滑动窗口中的中位数
- 思路:使用两个栈或优先队列维护窗口元素
-
[CSP-S 2019] 括号序列
- 难度:★★★★☆
- 描述:给定一个括号序列,求最少添加多少个括号能使序列合法
- 思路:使用栈模拟括号匹配过程,计算需要添加的括号数量
8.4 综合应用题
-
[USACO 2016 Feb Gold] Circular Barn
- 难度:★★★★★
- 描述:优化奶牛进入圆形牛棚的路径,最小化总行走距离
- 思路:使用单调队列或栈优化动态规划过程
-
[POJ 1028] Web Navigation
- 难度:★★★★★
- 描述:实现网页浏览器的前进、后退和访问新页面功能
- 思路:使用两个栈分别存储历史和前进记录
-
[CSP-J 2022] 解密
- 难度:★★★★★
- 描述:解密一段加密文本,需要按特定规则处理嵌套的加密结构
- 思路:使用栈处理嵌套结构,递归解析加密内容
栈(Stack)
